Introduction to Raptor Lake S and Raptor Lake S Refresh: Product Overview and Market Analysis
In the 11th month after the launch of the 12th generation Alder Lake S platform, Intel officially unveiled the 13th generation Intel Core Raptor Lake S platform. The Alder Lake S platform utilized a hybrid architecture with Performance cores (P-Cores) based on the Golden Cove microarchitecture and Efficiency cores (E-Cores) based on the Gracemont microarchitecture. The Raptor Lake S platform builds upon and further optimizes the Alder Lake S foundation, upgrading the Performance cores to the Raptor Cove microarchitecture while retaining the Gracemont microarchitecture for Efficiency cores.
For simplicity, we’ll refer to Alder Lake S as 12th Gen Core, Raptor Lake S as 13th Gen Core, and Raptor Lake S Refresh as 14th Gen Core throughout this article.
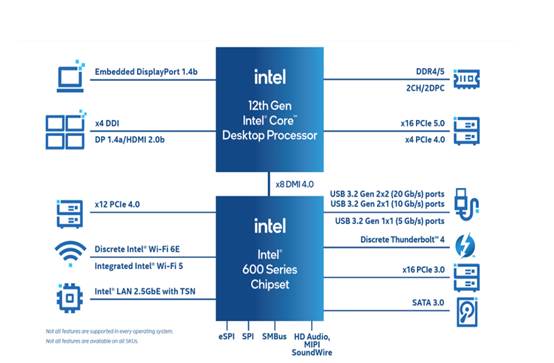
Architectural Improvements from 12th to 13th Generation
The 13th Gen Intel Core platform processors and Platform Controller Hub (PCH) fully support IoT software stacks. The LGA socket on 13th Gen Core products is compatible with previous generation products, allowing businesses to easily upgrade their systems. Specific SKU models feature larger L2 and L3 cache capacities, support for DDR5-5600 memory, PCIe 5.0 connectivity, and Intel Time Coordinated Computing (Intel TCC), while meeting Intel vPro standards. The 13th Gen Core processors feature improvements in manufacturing process, microarchitecture, and core count, offering users and gamers options with stronger performance and higher energy efficiency.
Advanced Connectivity and Memory Support
The platform provides maximum support for DDR5-5600 memory and PCIe 5.0 connectivity, enabling vendors to design powerful next-generation solutions that meet emerging application demands while being future-ready. The CPU provides up to 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes and 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes, allowing each processor to support more external accelerators or expansion cards. Meanwhile, the PCH offers up to 12 PCIe 4.0 lanes and up to 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes, further enhancing expansion flexibility. Systems based on 13th Gen Intel Core processors can quickly transfer and process large amounts of data, with higher I/O density supporting hardware integration and cost-effective deployment.
Backward Compatibility Advantages
In addition to backwards compatibility with DDR4 memory, the 13th Gen Core is also compatible with the previous generation 600-series motherboards. This means that 12th Gen Core users can upgrade to the 13th Gen without replacing their motherboards, while DDR4 versions of motherboards offer excellent value for money.
Raptor Lake S Refresh Platform
In the fourth quarter of 2023, Intel released the last processor with the “i” name – the Raptor Lake S Refresh platform, which as the name suggests is an upgraded version of the Raptor Lake S platform.
Manufacturing Process Advancements
Although still based on the Intel 7 process technology, Intel has continuously advanced its manufacturing techniques. Through improvements in lithography technology and optimization of transistor structures, they have increased chip performance and energy efficiency. This allows Raptor Lake S to achieve higher frequencies at the same power consumption or reduce power consumption at the same frequencies.# Introduction to Raptor Lake S and Raptor Lake S Refresh: Product Overview and Market Analysis
In the 11th month after the launch of the 12th generation Alder Lake S platform, Intel officially unveiled the 13th generation Intel Core Raptor Lake S platform. The Alder Lake S platform utilized a hybrid architecture with Performance cores (P-Cores) based on the Golden Cove microarchitecture and Efficiency cores (E-Cores) based on the Gracemont microarchitecture. The Raptor Lake S platform builds upon and further optimizes the Alder Lake S foundation, upgrading the Performance cores to the Raptor Cove microarchitecture while retaining the Gracemont microarchitecture for Efficiency cores.
For simplicity, we’ll refer to Alder Lake S as 12th Gen Core, Raptor Lake S as 13th Gen Core, and Raptor Lake S Refresh as 14th Gen Core throughout this article.
Architectural Evolution from 12th to 13th Generation
The 13th Gen Intel Core platform processors and Platform Controller Hub (PCH) fully support IoT software stacks. The LGA socket on 13th Gen Core products is compatible with previous generation products, allowing businesses to easily upgrade their systems. Specific SKU models feature larger L2 and L3 cache capacities, support for DDR5-5600 memory, PCIe 5.0 connectivity, and Intel Time Coordinated Computing (Intel TCC), while meeting Intel vPro standards.
The 13th Gen Core processors feature significant improvements in manufacturing process, microarchitecture, and core count, offering users and gamers options with stronger performance and higher energy efficiency.
Advanced Connectivity and Memory Support
The platform provides maximum support for DDR5-5600 memory and PCIe 5.0 connectivity, enabling vendors to design powerful next-generation solutions that meet emerging application demands while being future-ready. The CPU provides up to 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes and 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes, allowing each processor to support more external accelerators or expansion cards.
Meanwhile, the PCH offers up to 12 PCIe 4.0 lanes and up to 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes, further enhancing expansion flexibility. Systems based on 13th Gen Intel Core processors can quickly transfer and process large amounts of data, with higher I/O density supporting hardware integration and cost-effective deployment.
Backward Compatibility Advantages
In addition to backwards compatibility with DDR4 memory, the 13th Gen Core is also compatible with the previous generation 600-series motherboards. This means that 12th Gen Core users can upgrade to the 13th Gen without replacing their motherboards, while DDR4 versions of motherboards offer excellent value for money.
Manufacturing Process Innovations
Although still based on the Intel 7 process technology, Intel has continuously advanced its manufacturing techniques. Through improvements in lithography technology and optimization of transistor structures, they have increased chip performance and energy efficiency. This allows Raptor Lake S to achieve higher frequencies at the same power consumption or reduce power consumption at the same frequencies.
Raptor Lake S Refresh Platform
In the fourth quarter of 2023, Intel released the last processor with the “i” name designation – the Raptor Lake S Refresh platform. As the name suggests, this is an upgraded version of the Raptor Lake S platform, offering incrementally improved performance and efficiency while maintaining compatibility with existing motherboards.
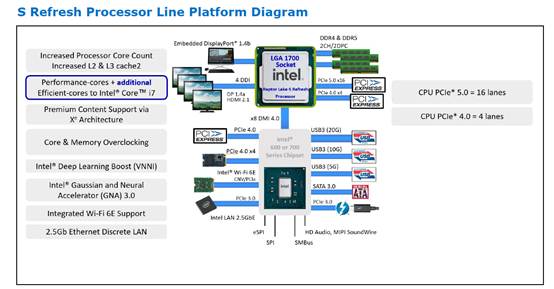
Core Configuration and Performance Enhancements
The 13th Gen processors feature significantly increased core counts compared to their predecessors, with flagship models offering up to 24 cores (8 P-cores and 16 E-cores). This substantial increase in core count, combined with the enhanced Raptor Cove microarchitecture, delivers impressive multi-threaded performance improvements over the 12th Gen processors.
The Raptor Cove P-cores feature improved branch prediction, wider execution units, and enhanced cache architecture, resulting in higher instructions per clock (IPC) compared to Golden Cove. Meanwhile, the E-cores continue to offer excellent power efficiency for background tasks and multi-threaded workloads.
AI and Voice Recognition Capabilities
With the growing importance of AI in modern computing, the 13th and 14th Gen Intel Core processors include improved neural processing units that accelerate AI workloads and voice recognition tasks. These capabilities enable more efficient handling of AI-based applications and voice assistant features in day-to-day computing.
Competitive Positioning in the Market
The Raptor Lake S and Raptor Lake S Refresh platforms represent Intel’s continued commitment to maintaining competitiveness in the high-performance desktop CPU market. These processors offer compelling options for a wide range of users, from gamers seeking high frame rates to content creators requiring multi-threaded performance for rendering and encoding tasks.
ALL In All
The 13th Gen Raptor Lake S and 14th Gen Raptor Lake S Refresh platforms demonstrate Intel’s iterative improvement approach, building upon the revolutionary hybrid architecture introduced with Alder Lake. By enhancing core microarchitectures, increasing core counts, expanding cache sizes, and maintaining backward compatibility, Intel has delivered competitive processors that cater to diverse computing needs while providing upgrade paths for existing customers.
The combination of high single-threaded performance from the Raptor Cove P-cores and efficient multi-threaded scaling from the Gracemont E-cores creates a versatile processor lineup capable of handling everything from gaming and productivity to content creation and AI-assisted workloads.
The image above illustrates the key architectural features of the Raptor Lake processors, highlighting the hybrid core design that forms the foundation of Intel’s modern CPU approach.